Educational resources for body, mind, and spirit.
Featured Video
Watch Dr. Raul Enad share his medical expertise and philosophy. In these discussions, he explores the intersection of Functional Medicine and bioethics.
Gain valuable insights into how we treat the whole person—body, mind, and soul—without compromising on faith or scientific rigor.
Visit YouTube ChannelExpert insights on health, lipidology, and faith.
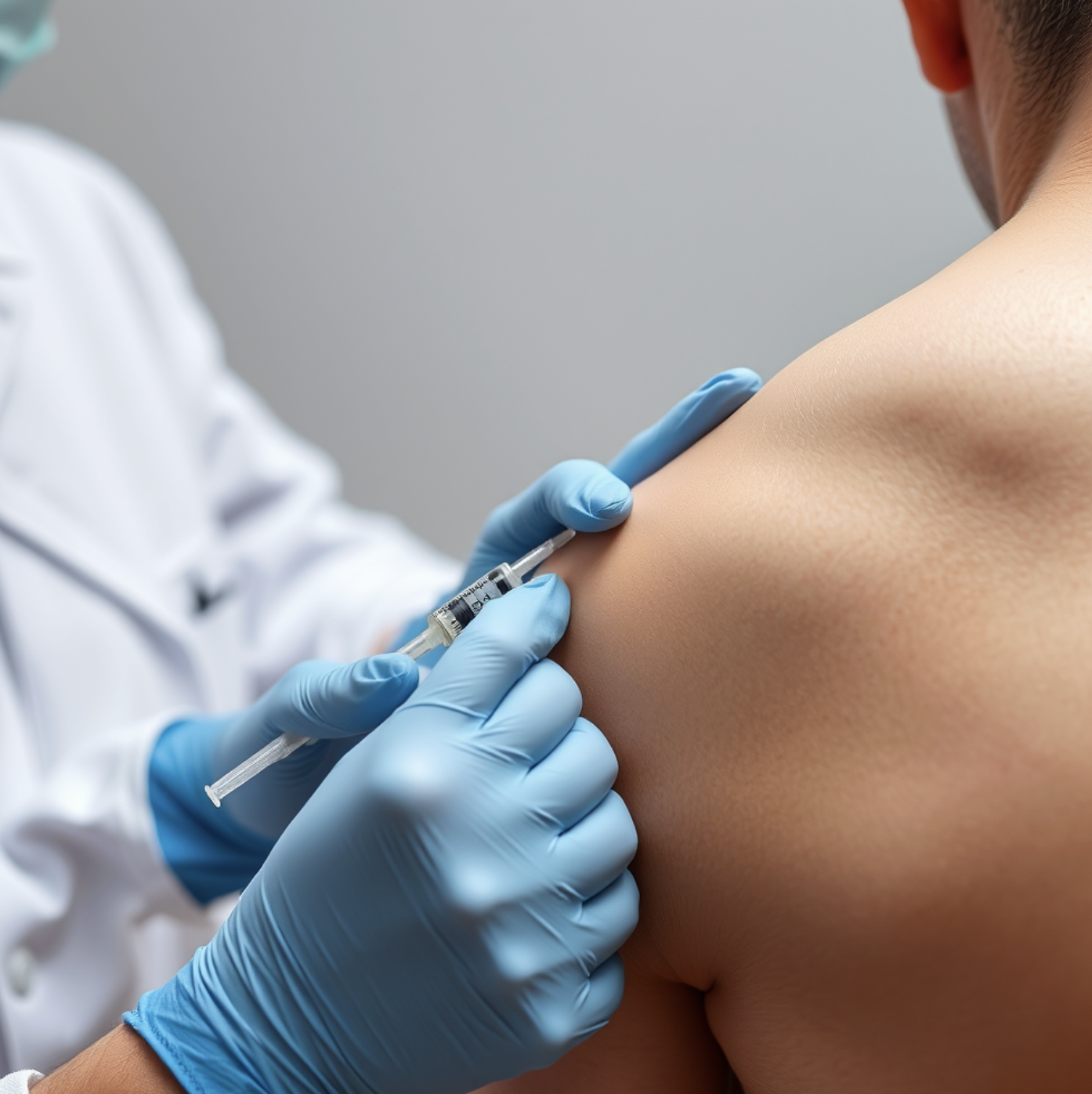
Health Insights
Discover how short-chain amino acids act as signaling molecules to promote tissue repair, cognitive function, and hormonal balance.
Read Article →
Theology of the Body
How acknowledging the spiritual dimension of the human person changes the way we diagnose and treat illness.
Read Article →
Health Insights
Anger is more than just an emotional response; it can have profound effects on your physical health, particularly on the cardiovascular...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Integrative medicine offers a holistic approach to healthcare, focusing on treating the whole person rather than just the disease. It...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Regenerative medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by offering innovative treatments that go beyond traditional methods of symptom
Read Article →
Health Insights
Aesthetic medicine has evolved from a luxury to a mainstream approach to enhancing one's appearance and boosting self-confidence.
Read Article →
Health Insights
The healthcare landscape offers a variety of options to suit different needs and preferences. Two primary models are concierge medicine...
Read Article →
Health Insights
IV therapy, also known as intravenous therapy, is a method of delivering fluids, medications, or nutrients directly into the bloodstream.
Read Article →
Health Insights
The importance of sleep for overall health is well-known, but its critical role in enhancing workout performance and recovery is often under
Read Article →
Health Insights
A robust immune system is essential for defending your body against infections and illnesses. While no single food or supplement can...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Regenerative medicine is a groundbreaking field that harnesses the body's inherent ability to heal itself. Instead of simply managing...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Tired of long wait times, rushed appointments, and feeling like just another number in the healthcare system? Concierge medicine offers a...
Read Article →
Health Insights
In today's world, the pursuit of beauty and self-confidence has led to remarkable advancements in aesthetic medicine. This rapidly...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Achieving peak exercise performance requires more than just dedication to your workouts; it demands a well-balanced diet tailored to support
Read Article →
Health Insights
Meditation, once considered a purely spiritual practice, has now found its place in the realm of science. Numerous studies have explored...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Intravenous (IV) therapy has become increasingly popular for its ability to deliver essential vitamins, minerals, and hydration directly...
Read Article →
Health Insights
The desire to look and feel your best is a natural human aspiration. While a consistent skincare routine is essential for maintaining a...
Read Article →
Health Insights
The world of medicine is on the cusp of a revolutionary breakthrough that could transform organ transplantation: lab-grown organs.
Read Article →
Health Insights
It's a familiar tale: you toss and turn all night, only to wake up craving a sugary, salty, or fatty treat. But why are sleepless nights...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Chronic pain can be debilitating, impacting your daily life and overall well-being. While traditional medicine offers effective pain...
Read Article →
Health Insights
IV therapy is generally considered safe when administered by trained professionals. It delivers essential nutrients and hydration...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Considering cosmetic surgery can be exciting, but it's a significant decision that shouldn't be taken lightly. Before you dive headfirst...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Living a healthy life can feel overwhelming, but it doesn't have to be complicated. Focusing on just three key habits can significantly...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Your first appointment with a concierge doctor is likely to be a comprehensive and personalized experience. Here’s what you can typically...
Read Article →
Health Insights
IV therapy for athletic performance has become increasingly popular, but there's mixed evidence on its effectiveness. Here's a breakdown...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Gene editing, particularly using CRISPR-Cas9 technology, holds significant promise for curing genetic diseases like cystic fibrosis.
Read Article →
Health Insights
Concierge medicine offers a tempting proposition: more time with your doctor, easier access to care, and potentially a more personalized...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Achieving a brighter, more youthful appearance doesn't always require surgery. Here are five popular non-surgical treatments that can...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Imagine your well-being as a triangle. Each side represents a crucial pillar: exercise, sleep, and diet. Just like a triangle, these...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Chronic pain can be debilitating, impacting your daily life and overall well-being. While traditional medicine offers effective pain...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Intravenous (IV) drips have become a popular method for delivering essential vitamins and minerals directly into the bloodstream,...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Aging is a beautiful part of life, but wrinkles can sometimes be a battle you'd rather win. When it comes to smoothing those lines, two...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Arthritis, characterized by joint inflammation and pain, affects millions of people worldwide. Traditional treatments often focus on...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Concierge medicine offers personalized healthcare services with varying costs based on the level of care provided. Here’s a comparison of...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Integrative medicine is an approach that combines conventional medical treatments with complementary therapies to address the whole...
Read Article →
Health Insights
The one-size-fits-all approach to healthcare is a thing of the past.
Read Article →
Health Insights
The healthcare landscape is undergoing a dramatic transformation, and telemedicine is at the forefront of this change. No longer...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Bioidentical Hormone Therapy (BHT) is a treatment designed to address hormone imbalances using hormones that are chemically identical to...
Read Article →
Health Insights
While the pursuit of a youthful appearance is a common desire, anti-aging treatments offer more than just wrinkle reduction. These...
Read Article →
Health Insights
The quest for youthful, radiant skin has driven significant advances in skin rejuvenation technologies and treatments. Innovations in...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Living with a chronic illness can feel like a daily challenge. But it doesn't have to define your life.
Read Article →
Health Insights
Medical weight loss programs are specialized, physician-supervised plans designed to help individuals achieve and maintain a healthy weight.
Read Article →
Health Insights
We all know the saying, "An ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure."
Read Article →
Health Insights
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a treatment used to alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances, particularly during...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Ever wondered how those injectable wrinkle relaxers work their magic? Cosmetic neurotoxins like Botox and Dysport have become popular...
Read Article →
Health Insights
IV therapy, or intravenous therapy, is rapidly gaining popularity as a revolutionary approach to wellness and health optimization....
Read Article →
Health Insights
Facial micro-needling with PRP, also known as a "vampire facial," is a popular treatment that combines micro-needling with platelet-rich...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Acne scars can have a significant impact on one's self-esteem and confidence. These scars, which often result from severe acne, can leave...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Functional medicine is an individualized, patient-centered approach to healthcare that focuses on identifying and addressing the root...
Read Article →
Health Insights
PRP, or Platelet-Rich Plasma, injections have become a popular option for treating joint pain and injuries. Here's a breakdown of the...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Regenerative medicine is a rapidly evolving field that harnesses the body's inherent ability to repair and regenerate tissues. This...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Internal medicine is a critical branch of medical practice that focuses on the comprehensive care of adults, covering a wide range of...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Aesthetic medicine is a branch of medical practice focused on enhancing physical appearance and addressing cosmetic concerns through...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Traditional healthcare can feel rushed and impersonal. Long wait times, limited appointment slots, and fragmented care can leave you...
Read Article →
Health Insights
The concept of "one size fits all" doesn't apply to healthcare. Our bodies, needs, and goals are unique, and so should be our approach to...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Functional medicine is a holistic approach to healthcare that combines conventional Western medicine with complementary and alternative...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Achieving radiant, youthful skin is a common goal for many, and advancements in dermatology have made it more attainable than ever. Skin...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Telemedicine, the practice of providing medical care remotely through telecommunications technology, has revolutionized the healthcare...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Bioidentical hormone therapy (BHRT) has become a popular option for managing symptoms associated with hormonal decline. Here at Cadenza...
Read Article →
Health Insights
In today's fast-paced world, stress and anxiety have become common adversaries that many of us face on a daily basis. The constant...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Achieving and maintaining a healthy weight is crucial for overall well-being, but for many, it can be a challenging journey. Medical...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Here's a breakdown of some popular anti-aging treatments to consider, keeping in mind that some may require a consultation with a...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Living with a chronic illness can be challenging, but you don't have to go it alone. By taking a proactive approach and implementing some...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Hormone Replacement Therapy (HRT) is a medical treatment used to alleviate symptoms associated with hormonal imbalances or deficiencies,...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Imagine a world where you prioritize your health not just when you're feeling unwell, but throughout your life. That's the power of...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Intravenous (IV) therapy, once primarily used in hospitals for hydration and delivering medications, has gained popularity in recent...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Both Botox and Dysport are injectable wrinkle relaxers, but there are some key differences to consider when deciding which one is right...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Acne is a common skin condition that can leave behind scars, affecting both appearance and self-confidence. While preventing acne is...
Read Article →
Health Insights
PRP, or Platelet-Rich Plasma, injections have become a popular option for treating joint pain and injuries. But what exactly are...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Facial micro-needling with Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP) is a cutting-edge aesthetic treatment that combines the benefits of micro-needling...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Internal medicine plays a pivotal role in the realm of comprehensive healthcare, focusing on the prevention, diagnosis, and treatment of...
Read Article →
Health Insights
At Cadenza Med Clinic, we believe in a comprehensive approach to healthcare that goes beyond just treating symptoms. That's where...
Read Article →
Health Insights
Regenerative medicine is revolutionizing healthcare by harnessing the body's natural healing capabilities to repair or replace damaged...
Read Article →
Health Insights
In the fast-paced world of modern healthcare, many patients find themselves feeling like just another number in a crowded waiting room....
Read Article →
Health Insights
In today’s beauty-centric world, aesthetic medicine offers numerous treatments to help rejuvenate your look and boost your confidence....
Read Article →